
Ĭompetent calculations of excited states properties are emerging field of interest for quantum chemists hence, they are developing interesting solutions for these properties. Over the last years, DFT advanced by the capability to include effects of electron correlation in a very effectual means to the forefront of field of calculating NMR parameters. For speculations of NMR parameters, a practical approximation of the real system is depicted by a model system in which 50–100 atoms are treated with ab initio techniques. It is obvious that local geometrical and electronic structures influence magnetic resonance parameters, i.e., shielding tensors, nuclear spin-spin coupling parameters, hyperfine tensors and g-tensors. Taking NMR spectroscopy into consideration, DFT-based new methods are developed that are appropriate for the satisfactory hypothetical interpretation of NMR spectra of various chemical and biochemical systems. Calculation of optimized geometry, IR intensities, vibrational frequencies and Raman scattering activities can be done by employing different density functional approaches. DFT largely overcome the errors as theoretical computations helped to interpret experimental conclusions depicting that using DFT these theoretical data can nearly be attained at the harmonic level. Inadequate handling of electron correlation and anharmonicity of the vibrations are found to be the main contributions to error. Previously, the HF method was used in many studies to calculate vibrational frequencies, but it has long been identified that this approach miscalculates these frequencies even occasionally to a disturbing degree. įor experimental spectroscopists, theoretical computation of vibrational frequencies has become practically essential these days as specifically in problematic and uncertain cases it assists to assign and interpret experimental infrared/Raman spectra. Functionals available today can strive with best previous ab initio methods. For calculation of the molecular and electronic structures of ground-state systems and various spectral parameters related to NMR, ESR, UV-Vis and IR, various density functional practices are available now. Much advancement has been made in the past decade to design new DFT approaches that can be employed into available quantum-chemical computational programs. Prediction of frequencies and spectral intensities by DFT calculations are indispensable nowadays for interpreting the experimental spectra of complex molecules. Spectroscopic analysis of chemical entities by this technique emerged as commanding implementation. The density functional theory (DFT) has become a powerful tool in computational chemistry owing to its usefulness. The reference orbitals determined by a set of operative one-particle Schrodinger-wave equations are called Kohn-Sham (KS) equations one of them is depicted in Eq. (1). The work of Kohn and Sham instantly surveyed and paved the way for hands-on computational applicability of DFT to physical systems, by linking a reference-state comprising of a set of noninteracting one-particle orbitals with a particular functional.

The second theorem verifies that total electric energy of the system E is minimalized by the ground state density. The first theorem demonstrates a many-particle system n(x,y,z) for which one-to-one plotting happens between the ground state electric density and the ground state wave function. The Hohenberg-Kohn theorems state that the exact ground state energy of the system is produced by a unique functional of the electron density ρ. Although such theories and techniques proved beneficial, it was density functional theory (DFT) that laid a demanding theoretical foundation in 1964 by an outstanding result established by Hohenberg and Kohn. HF theory was a simplest ab initio technique and among the first principles of quantum-chemical theories, being attained directly from the Schrodinger-wave equation that did not incorporate any pragmatic contemplations.
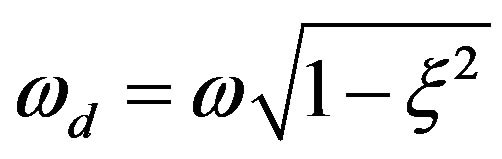
Early days of quantum chemistry go back to Thomas-Fermi and Thomas-Fermi-Dirac models of the electronic structure of atoms, which gave the concept of articulating some parts or all of the molecular energy as a functional of the electron density, and then comes the traditional Hartree-Fock (HF) theory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
